What is Calcium Carbonate
 Calcium carbonate is a white powder commonly found in rocks and in shells of marine and land organism, pearls, and egg shell. The main applications of calcium carbonate are in paper, construction industry, paints, plastics, ceramics and food. It is also found in agricultural lime which adjusts soil properties and acts as a fertilizer. It is commonly used as a calcium supplement or antacid.
Calcium carbonate is a white powder commonly found in rocks and in shells of marine and land organism, pearls, and egg shell. The main applications of calcium carbonate are in paper, construction industry, paints, plastics, ceramics and food. It is also found in agricultural lime which adjusts soil properties and acts as a fertilizer. It is commonly used as a calcium supplement or antacid.
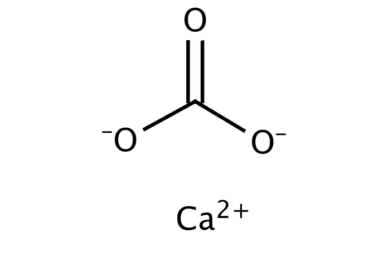
Calcium carbonate is a chemical compound with the formula CaCO3. It is a common substance found in rocks as the minerals calcite and aragonite (most notably as limestone, which is a type of sedimentary rock consisting mainly of calcite) and is the main component of pearls and the shells of marine organisms, snails, and eggs. Calcium carbonate is the active ingredient in agricultural lime and is created when calcium ions in hard water react with carbonate ions to create limescale. It is medicinally used as a calcium supplement or as an antacid, but excessive consumption can be hazardous.
Calcium carbonate causes a unique reaction with acids. Upon contact with an acid – no matter the strength – it produces carbon dioxide. This provides geologists with a reliable test to identify calcium carbonate. This same phenomenon is important to the formation of caves. Acidic rain water runs off and goes underground where it dissolves the calcium carbonate limestone. The calcium carbonate water runs down and eventually reaches an air-filled cavity underground where the carbon dioxide can be released. When it is released, the calcium carbonate crystallizes again. Stalactite and stalagmite formations are created when water containing calcium carbonate drips, leaving some mineral at the source of the drip at the roof of the cave and some where it falls. This is an extremely long process, and often takes place over many thousands of years.
Structure
The thermodynamically stable form of CaCO3 under normal conditions is hexagonal β-CaCO3 (the mineral calcite). Other forms can be prepared, the denser (2.83 g/cm3) orthorhombic λ-CaCO3 (the mineral aragonite) and hexagonal μ-CaCO3, occurring as the mineral vaterite. The aragonite form can be prepared by precipitation at temperatures above 85 °C, the vaterite form can be prepared by precipitation at 60 °C. Calcite contains calcium atoms coordinated by six oxygen atoms, in aragonite they are coordinated by nine oxygen atoms. The vaterite structure is not fully understood. Magnesium carbonate (MgCO3) has the calcite structure, whereas strontium carbonate and barium carbonate (SrCO3 and BaCO3) adopt the aragonite structure, reflecting their larger ionic radii.
Manufacturing Process

MIXING
BUBBLING
AGITATION
MIXING
The initial step of calcium carbonate manufacturing (primarily the precipitated calcium carbonate) is to mix the calcium ions source with a solvent to create slurry
BUBBLING
The slurry obtained from the mixing process is fed into a reactor and carbonated by bubbling carbon dioxide gas stream at a pressure above atmospheric pressure
AGITATION
After bubbling the mixture, the agitation is conducted to quickly obtained the calcium carbonate from the mixture of soluble calcium ions and carbonate ions at certain temperatures, slurry concentration, and pressure to obtain specific properties from the calcium carbonate generated
The Uses of Calcium Carbonate
Calcium carbonate crystals are referred to as calcite. The calcite crystal generally is considered a rhombohedron because of its cleavage properties. Cleavage is what causes crystals to angle where the bonding forces are weak and are apt to break into planes. Calcite is unique in that its cleavage takes three distinct directions. There are more than 300 forms of calcite crystals.

Agriculture
Calcium carbonate in agricultural applications is used as a neutralizer to neutralize acidic soil, thus increasing the productivity of crops.

Pharmaceutical
To whiten drugs, the pharmaceutical industry used calcium carbonate both as a color additive and dietary supplements for calcium deficiency.

Glass and Ceramic
Calcium carbonate is used as whiting for ceramic glaze which acts as a flux to lower the melting point of glass-forming constituent.

Food and Beverage
Having an E number from European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), calcium carbonate is classified as a colorant, particularly as a white colorant in the food industry with an E number of E170.
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
- CAS NO.
- FORMULA
- MOL WT.
- SYNONYMS
- 471-34-1
- CaCO3
- 100.0869 g/mol
- Limestone, calcite, aragonite, chalk, marble
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
- PHYSICAL STATE
- MELTING POINT
- BOILING POINT
- SOLUBILITY IN WATER
- DENSITY AND PHASE
-
ALKALINITY
- White, powdered solid, odourless
- 1339 °C (calcite), 825 °C (aragonite)
- Decomposes
- 0.0013 g/100mL (25°C)
-
2.711 g/cm3, (calcite),
2.83 g/cm3, (aragonite) - Alkaline (pH 9.9)
